Core Technology
Core Technology
Complete process
Core Equipment
Catalyst
Propylene Oxide/Styrene Cogeneration Technology (RHPOSM)
Summary:
Propylene oxide is the third largest propylene derivative after polypropylene and acrylonitrile. It is mainly used in the production of polyether, propylene glycol, etc. Its derivatives are widely used in automobile, construction, food, tobacco, medicine and cosmetics industries. Nearly 100 kinds of downstream products have been produced, which are important raw materials for fine chemical products.
Classification:
Key words:
Detailed description
Propylene oxide is the third largest propylene derivative after polypropylene and acrylonitrile. It is mainly used in the production of polyether, propylene glycol, etc. Its derivatives are widely used in automobile, construction, food, tobacco, medicine and cosmetics industries. Nearly 100 kinds of downstream products have been produced, which are important raw materials for fine chemical products.
Industrial propylene oxide production technology mainly has chlorohydrin method and indirect oxidation method. The production of propylene oxide by chlorohydrin method is characterized by relatively short process, mature process and low construction investment. However, a large amount of wastewater containing calcium chloride will be produced in the process of producing propylene oxide by chlorohydrin method, and the environmental pollution is very serious. Therefore, China has stopped the approval of new chlorohydrin propylene oxide plant since 2011.
At present, all domestic propylene oxide units using indirect oxidation process adopt foreign technology. Changzhou Ruihua Chemical has incorporated indirect oxidation propylene oxide technology into the scope of research and development since its establishment. After five years of development, it has successfully developed complete sets of process technologies for propylene oxide/styrene co-production (PO/SM) and propylene oxide/styrene co-production (PO/AMS).
Process
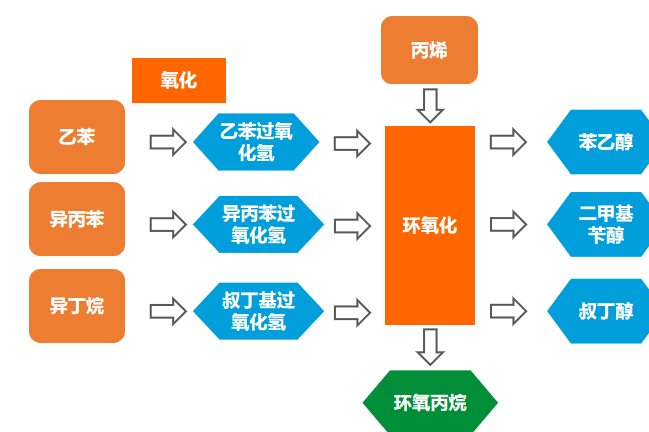
The process of propylene oxide/styrene co-production includes ethylbenzene peroxidation, epoxidation, phenylethanol dehydration and acetophenone hydrogenation.
Ethylbenzene peroxidation was carried out in three bubble column reactors. The liquid phase ethylbenzene enters the first reactor, and the air enters the three reactors respectively. The ethylbenzene reacts in the reactor to produce ethylbenzene hydrogen peroxide. After reaching a certain concentration, it enters the next reactor. After three reactors, the content of ethylbenzene hydrogen peroxide in the material is about 11-13%, and then it enters the concentration tower to increase the concentration of peroxide and enters the epoxidation reactor for reaction.
The epoxidation reactor is a plurality of horizontal reactors connected in series. Liquid phase propylene enters the first reactor and then the next reactor in turn, while ethylbenzene hydroperoxide enters each reactor separately. In the epoxidation reactor, propylene is oxidized to propylene oxide and ethylbenzene hydroperoxide is converted to phenethyl alcohol and acetophenone. After propylene is recovered from the epoxidized product, crude propylene oxide is separated, and then after light removal, heavy removal and extraction separation, polymerization grade propylene oxide is obtained.
The acetophenone produced by epoxidation is hydrogenated to produce phenethyl alcohol, which is dehydrated to produce styrene. After purification and separation of crude styrene, polymer grade styrene is obtained.
Feed requirements
The raw material ethylbenzene for POSM process must be alkylated with vinylbenzene, and the purity of ethylbenzene is> = 99.8. Raw material propylene shall meet the requirements of GB 7716-2002 for superior products.
Recommended Information
Next
Next
0nline message
Contact us

5/F, Block A, Building 1, Chuangyan Port, Science and Education City, Wujin District, Changzhou City, Jiangsu Province
Copyright© 2024 Ruihua Chemical






















